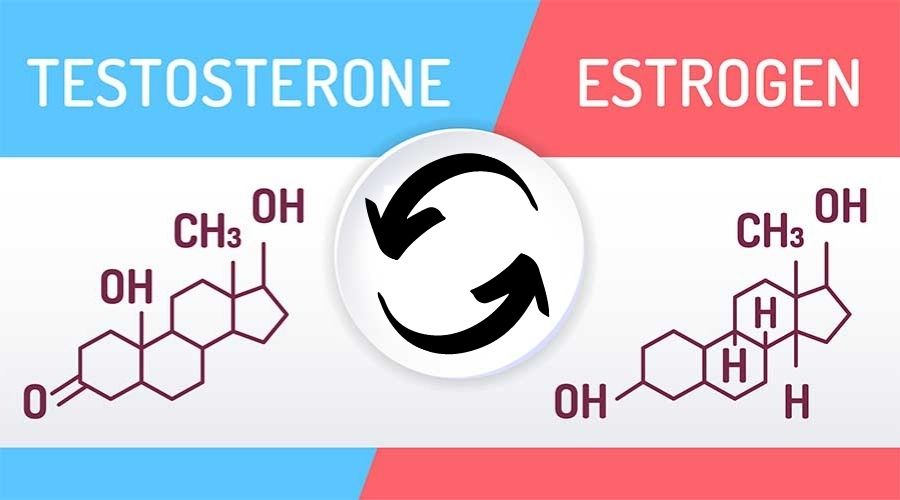
A man’s body normally produces about 45 micrograms of estrogen per day via a process called aromatization.
That’s a natural process that occurs mainly in your fat tissue but also in your bones, brain, arteries, liver, and testes.
An enzyme called aromatase resides there and it converts some of your testosterone into estrogen in order to maintain a balance between the two hormones.
This balance is key for the normal function of a man’s body, since estrogen plays an important role in male sexual development, mood, bone mineral density, and hormonal regulation.
Therefore, both too low and too high estrogen levels can lead to health problems and require proper treatment.
Here’s how to stop the aromatization of testosterone and which medications and natural estrogen blockers are most effective.
What causes the aromatization of testosterone?
There are several types of estrogen but E1 (estrone) and E2 (estradiol) are the main ones seen in men. Aromatization is caused by large fluctuations in testosterone production and violation of the estrogen-testosterone balance.
Estradiol is the most potent form of estrogen in the male body
The process of aromatization occurs all the time in healthy individuals since estrogen is needed for several physiological functions. For example, E2 plays a major role in increasing bone mineral density during puberty and then maintaining it throughout life.
Estradiol also acts as negative feedback for the production of gonadotropic hormones from the pituitary gland. Those are the follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) which regulate testosterone synthesis in the testes.
If T levels rise, more of it will be converted to E2. This increases estrogen’s suppressive effect on FSH and LH which reduces testosterone back to normal ranges.
The level of inhibition depends on whole-body E2 levels, including the amount aromatized in your fat tissues. If you have too much body fat this means you likely have higher activity of the aromatase enzyme as well.
Therefore, a higher percentage of your testosterone will be converted into estrogen. The latter will suppress FSH and LH leading to low T but normal or elevated E2 levels.
Heavy chronic alcohol consumption may also increase the activity of the enzyme and increase estrogen levels
Can testosterone therapy increase estrogen levels?
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is an FDA-approved treatment for men with low T. It requires regular application of exogenous testosterone, which has the same benefits and potential to get aromatized in your body as naturally produced T.
Legal TRT prescribed by a medical doctor may also increase your estrogen, but it is not likely to cause high E2 levels.
It aims to maintain serum T levels in the mid-normal range, which ensures that your estrogen levels will also remain within references. The rate of conversion is dose-dependent, and higher doses of TRT will also lead to higher estradiol levels.
Proper T dosing is key for preventing high estrogen levels during treatment
Always follow your doctor’s recommendations and avoid increasing your dose without medical consultation.
Over-the-counter testosterone products such as herbal extracts and supplements have unreliable hormonal effects. The majority of their ingredients may be ineffective since they lack scientific support while 10% may even reduce T levels. The effects on estrogen levels remain largely unstudied.
What are the side effects of aromatization?
Normal estrogen levels in men should be in the range of 10-40 pg/ml. E2 above the upper range may lead to symptoms, especially if it is in combination with low T levels.
Studies reveal that high estradiol levels may cause sexual problems such as erectile dysfunction. On the other hand, too low estrogen may result in delayed ejaculation or an inability to reach a climax at all.
Read Next: How Ejaculation/Masturbation Affects Testosterone Levels
In male adolescents, high estradiol may lead to premature closure of the epiphyseal plates and short stature in men.
According to researchers, maintaining estradiol within an optimal range is also important for normal spermatogenesis. If estrogen is too high it may lead to infertility.
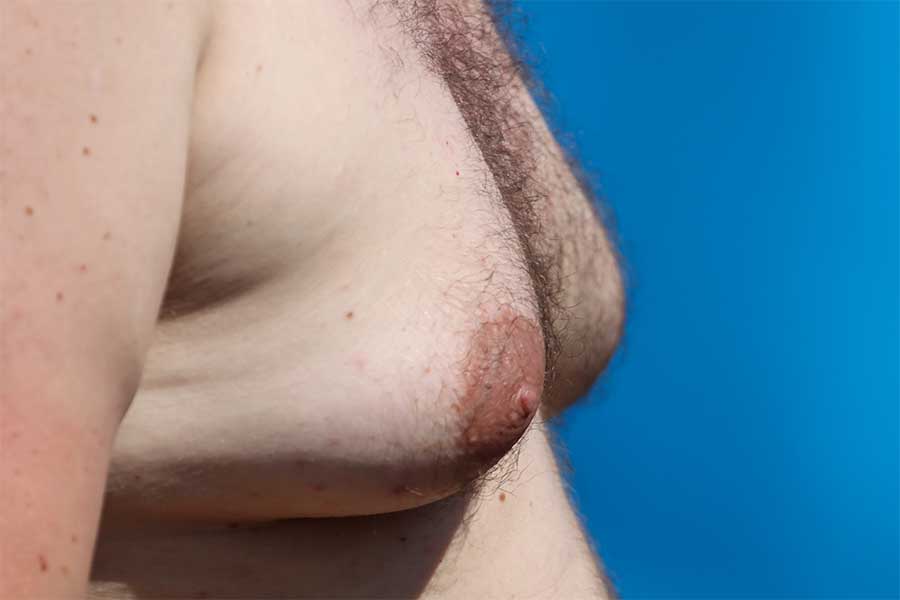
Furthermore, significantly elevated estrogen may lead to swelling or enlargement of breast tissue.
The condition is also known as gynecomastia and its initial signs develop after 3-6 months of exposure to elevated estrogen levels. Studies report that it takes 6-9 months for gynecomastia to fully develop.
At first, it develops as increased sensitivity and tenderness around the mamilla which is reversible. If left unchecked it turns into swelling and gynecomastia which is no longer completely reversible and has to be treated surgically.
The degree of aromatization and thus estrogen levels tend to increase with age. This may contribute to sexual problems and reduced fertility which are more common in middle-aged and older men. This is why some men use hCG instead of testosterone injections to maintain their fertility.
Get a free consultation with our medical expert for any questions about hormone replacement therapy