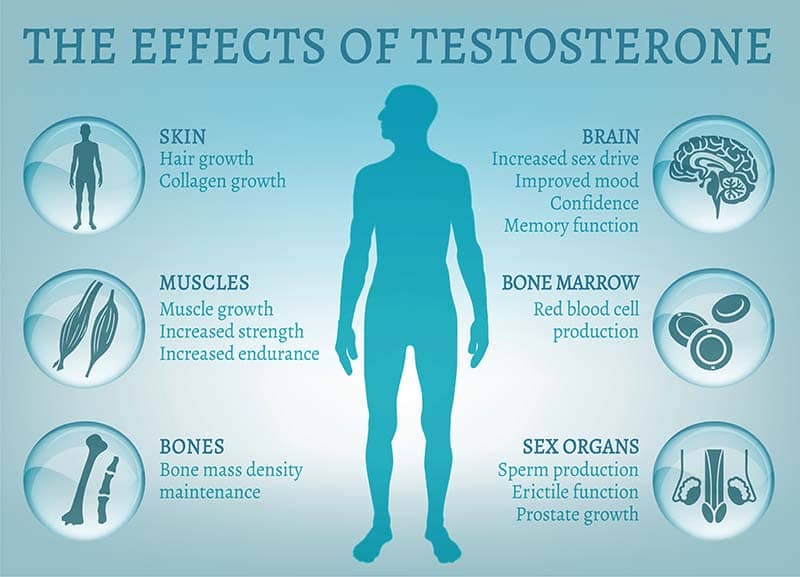
Testosterone (T) is the male sex hormone. It is important for normal sexual and erectile function, maintaining muscle mass, energy levels, and even mental wellbeing.
Testosterone levels usually peak around your 20s and then gradually drop as you age by 1% per year on average. Unfortunately, some men might experience symptoms, once their T levels drop under a certain threshold.
Low T can lead to debilitating symptoms such as erectile dysfunction, increase in body fat, mental and cognitive problems. These symptoms can be successfully reversed by testosterone replacement therapy (TRT).
What is testosterone therapy and how does it work?
TRT is the treatment of choice for the management of low T symptoms. Testosterone therapy can effectively increase T levels in the body back to normal.
Replacement therapy should aim at achieving blood levels of testosterone in the middle to the upper part of the normal reference range. Testosterone can be delivered successfully in the body via various routes and thus it comes in multiple forms:
- Injections
- Skin or mouth patches
- Skin and nasal gels
- Oral (Pills)
- Implants (Pellets)
TRT is usually prescribed to men above the age of 40 since problems with T levels typically become more common. However, treatment can be started at any age if there are medical conditions that require it and no contraindications.
Do you need testosterone therapy?
The doctor will determine whether you need TRT by assessing your symptoms and assigning you diagnostic tests. TRT can be prescribed to people with low T levels and symptoms.
The condition of having low T is called hypogonadism and can be categorized as one of two types – primary or secondary hypogonadism.
In the case of primary hypogonadism, the testicles are unable to produce enough testosterone even under an increased stimulus by the pituitary gland. Causes of primary hypogonadism include:
- Tumor, surgery, trauma, radiation, or infection affecting the testicles
- Genetic conditions (such as Klinefelter’s syndrome)
- Anatomical causes (cryptorchidism, varicocele)
- Late-onset hypogonadism (andropause)
Secondary hypogonadism develops due to a lack of hormonal stimulus from the pituitary gland to the testicles. Thus the initial problem is in the pituitary gland but it eventually leads to testicular atrophy. The main causes of secondary hypogonadism include:
- Tumor, surgery, trauma, radiation, or infection affecting the pituitary gland
- Genetic conditions (Kallmann syndrome)
- Drugs and anabolic steroid abuse
In men, the symptoms of hypogonadism are:
- Erectile dysfunction and low libido
- Infertility
- Muscle loss
- Fat gain
- Depression and mood problems
- Cognitive problems
- Anemia (low red blood cells)
- Low energy levels and fatigue
- Loss of body and facial hair
The diagnostic process of hypogonadism
For the diagnosis, your doctor will measure the blood levels of T in the morning when normal T production should be at its highest. Total T levels below 300 ng/dL in men indicate hypogonadism.
Tests must be repeated at least once to confirm the diagnosis. If the hypogonadism is confirmed, then additional tests can categorize it as primary or secondary.
They include measuring the gonadotropic hormones produced by the pituitary gland such as luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
According to the guidelines, high LH and FSH indicate primary hypogonadism. If they are normal or low, this is a sign of a pituitary problem and suggests secondary hypogonadism.
The proper diagnosis of low testosterone requires careful assessment of your symptoms and multiple hormonal tests to correctly identify the cause of your problems.
How to get a legal testosterone treatment
Testosterone is a prescription medication regulated by the FDA because it can be abused as a performance-enhancing drug due to its anabolic effects. Thus, obtaining low T treatment requires a prescription from a medical doctor.
Typically prescribed forms include injections, implants, and gels
Testosterone injections are the most commonly prescribed form since they are the easiest to dose and lead to the quickest rise in blood T levels. Thus, they are the most effective and reliable method to achieve the desired levels of testosterone.
Besides, injections are considerably safer than pills because oral forms of testosterone pass through the liver first where they are metabolized and might be hepatotoxic.
Your physician will determine what is the best form of TRT and offer a legal testosterone prescription only if your medical exam and diagnostic tests indicate hypogonadism.
Who shouldn’t take TRT?
Make sure to notify your doctor if you are planning to have children in the near future. Low T treatment can suppress the production of LH, FSH, endogenous testosterone, and spermatogenesis.
Besides, therapy may aggravate certain preexisting health conditions which can lead to serious complications. The Endocrine Society states that TRT is contraindicated in the case of:
- problems with the lower urinary tract (due to enlarged prostate)
- increased risk of prostate or breast cancer
- elevated red blood cell count or thrombocytes
- severe obstructive sleep apnea
- congestive heart failure
- recent (in the last 6 months) myocardial infarction or stroke
What to expect from testosterone therapy?
Patients on TRT experience improvements in sexual function, libido, erections, muscle mass, fat loss, energy levels, mood, and cognition. The therapy can also help with reversing anemia and low bone mineral density in hypogonadal men.
Unfortunately, low T treatment is not free of side effects. Studies report that the most common adverse reactions include elevated red blood cell count, increased urination, oily skin, acne, and reduced sperm count. Conditions such as prostate enlargement can become worse on TRT.
The evidence is still inconclusive on whether TRT increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
If you have any preexisting cardiovascular conditions make sure to warn your doctor
TRT’s safety and effectiveness should be carefully monitored by an experienced medical doctor for the whole duration of the treatment.
The results of TRT occur gradually over time and thus long-term therapy might be optimal to successfully reverse all symptoms of low T.
How long should therapy last?
According to the scientific literature on TRT, the first benefits occur at least 3 weeks after the start of the treatment and include improved libido, mood, and quality of life.
It takes 4 weeks of TRT for cholesterol levels to improve. An increase in muscle mass, fat loss, red blood cell count, and insulin sensitivity occur after at least 3 months. Bone mineral density can also improve after 6 months.
Erectile function is also improved after 6 weeks of therapy on average
Currently, there is no recommendation on how long a TRT should last. Your doctor will estimate the length of your therapy based on its effectiveness and the occurrence of adverse reactions.
The long-term safety of low T treatment reports that there haven’t been any significant adverse effects due to prolonged treatment. In fact, one 11-year long trial in obese men revealed that the group on TRT had lower mortality when compared to placebo.
How much will therapy cost you?
The length of the therapy is the main factor that determines its total cost. Your TRT might cost between $100 and $1000 per month depending on the brand, dosage, and pharmaceutical form you are prescribed. What’s more, in some states you can buy testosterone injections online if you have a prescription, which can make your treatment more affordable.
Initially, you will have extra expenses for testing and a medical exam. It will cost you around $100 to visit an experienced specialist.
Measuring your total T levels costs about $50 and an extra $50 if the test includes free T. There might be additional lab tests to rule out contraindications such as PSA, hematocrit, etc. which also contribute to the total price.
Get a free consultation with our medical expert for any questions about hormone replacement therapy